Телефонные коды городов
Франции . Обратите внимание, некоторые города могут иметь несколько кодов, тогда коды указаны через запятую. Телефонные коды других стран смотрите на странице коды стран
Порядок набора телефонного номера для Франции (код 33 = код Франции)
Как позвонить в Францию?
С городского: 8-гудок-10-33-(код города)-(телефонный номер абонента)*
С городского (внутри страны): 8-гудок-(код города)-(телефонный номер абонента)
С мобильного: +33-(код города)-(номер телефона абонента)**
* при звонке из страны с кодом «33» код страны (из которой совершаете звонок совпадает с кодом страны куда хотите позвонить) в большинстве случаев нужно опускать, так же как и код выхода на международную связь (код 10 — код выхода на международную связь, код зависит от оператора связи)
** набирать «+» или «8» перед кодом страны, зависит от мобильного оператора.
| Наименование | Код страны | Код города |
| Авиньон | 33 | (49) |
| Ажен | 33 | (553) |
| Алансон | 33 | (233) |
| Альби | 33 | (563) |
| Амьен | 33 | (322) |
| Ангулем | 33 | (545) |
| Анже | 33 | (241) |
| Аннеси | 33 | (450) |
| Антиб | 33 | (493) |
| Арль | 33 | (490) |
| Аррас | 33 | (321) |
| Аяччо | 33 | (495) |
| Бар-ле-Дюк | 33 | (329) |
| Безансон | 33 | (381) |
| Белен | 33 | (479) |
| Бельфор | 33 | (384) |
| Блуа | 33 | (254) |
| Бобиньи | 33 | (14) |
| Бове | 33 | (344) |
| Бордо | 33 | (556) |
| Бурж | 33 | (248) |
| Бурк-ан-Брас | 33 | (474) |
| Валянс | 33 | (475) |
| Ванн | 33 | (297) |
| Везуль | 33 | (384) |
| Версаль | 33 | (13) |
| Вильфранш-Сюр-Сон | 33 | (474) |
| Вьенна | 33 | (474) |
| Гап | 33 | (492) |
| Гере | 33 | (555) |
| Гренобль | 33 | (476) |
| Дижон | 33 | (380) |
| Динь | 33 | (492) |
| Драгиньян | 33 | (494) |
| Дюнкерк | 33 | (328) |
| Кан | 33 | (231) |
| Каор | 33 | (565) |
| Каркассон | 33 | (468) |
| Кемпер | 33 | (298) |
| Клермон-Ферран | 33 | (473) |
| Кольмар | 33 | (389) |
| Кретей | 33 | (14) |
| Ла-Рош-Сюр-Ион | 33 | (251) |
| Ла-Рошель | 33 | (546) |
| Лаваль | 33 | (243) |
| Лан | 33 | (323) |
| Ле-Ман | 33 | (243) |
| Ле-Пюи | 33 | (471) |
| Ленгви | 33 | (382) |
| Либурн | 33 | (557) |
| Лилль | 33 | (320) |
| Лимож | 33 | (544) |
| Лион | 33 | (437) |
| Лон-Ле-Сонье | 33 | (384) |
| Макон | 33 | (385) |
| Манд | 33 | (466) |
| Марсель | 33 | (491) |
| Мелен | 33 | (160) |
| Мец | 33 | (387) |
| Мон-де-Марсан | 33 | (558) |
| Монблан | 33 | (563) |
| Монпелье | 33 | (467) |
| Монте Карло | 33 | (493) |
| Мулен | 33 | (470) |
| Нанси | 33 | (383) |
| Нант | 33 | (240) |
| Нантер | 33 | (14) |
| Невер | 33 | (386) |
| Ним | 33 | (466) |
| Ницца | 33 | (493) |
| Ньор | 33 | (549) |
| Оза | 33 | (562) |
| Орийак | 33 | (471) |
| Орлеан | 33 | (238) |
| Осер | 33 | (386) |
| Оуа | 33 | (561) |
| Париж | 33 | (1) |
| Периге | 33 | (553) |
| Перпиньян | 33 | (468) |
| По | 33 | (559) |
| Понтуаз | 33 | (13) |
| Прива | 33 | (475) |
| Пуатье | 33 | (549) |
| Пюи-де-Дрм | 33 | (3371) |
| Ренн | 33 | (223) |
| Родез | 33 | (565) |
| Руан | 33 | (235) |
| Рубе | 33 | (327) |
| Сен Брие | 33 | (296) |
| Сен-Ло | 33 | (233) |
| Сент Этьен | 33 | (477) |
| Страсбург | 33 | (390) |
| Тарб | 33 | (562) |
| Труа | 33 | (325) |
| Тулон | 33 | (498) |
| Тулуза | 33 | (534) |
| Тур | 33 | (247) |
| Тьонвиль | 33 | (382) |
| Тюль | 33 | (555) |
| Фуа | 33 | (561) |
| Шамберн | 33 | (479) |
| Шартр | 33 | (237) |
| Шатору | 33 | (254) |
| Шомон | 33 | (325) |
| Эвре | 33 | (232) |
| Эври | 33 | (16) |
| Экс Ан Прованс | 33 | (442) |
| Эпиналь | 33 | (329) |
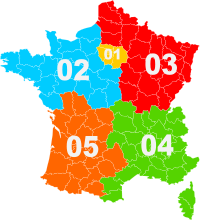 5 geographic zones | |
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Country | France |
| Continent | Europe |
| Regulator | ARCEP |
| Type | Closed |
| NSN length | 9 |
| Format | 0x xx xx xx xx |
| Access codes | |
| Country calling code | 33 |
| International call prefix | 00 |
| Trunk prefix | 0 |
The French telephone numbering plan is used in Metropolitan France, French overseas departments and some overseas collectivities.
France uses a ten-digit closed numbering plan, where the first two digits denote a geographic area, mobile or non-geographic number.
- 01 Île-de-France
- 02 Northwest France
- 03 Northeast France
- 04 Southeast France
- 05 Southwest France
- 06 Mobile phone services
- 07 Mobile phone services
- 08 Special phone numbers: Freephone (numéro vert) and shared-cost services.
- 09 Non-geographic number (used by Voice over IP services)
All geographic numbers are dialed in the ten-digit format, even for local calls. The international access code is the International Telecommunication Union’s recommended 00.[1]
When calling France from abroad, the leading zero should be omitted: for example, to call a number in Southwest France, one would dial +33 5 xx xx xx xx.
French people usually state phone numbers as a sequence of five double-digit numbers, e.g., 0x xx xx xx xx (and not, for example, 0 xxx-xxx-xxx or 0xxx-xx-xxxx or 0xx-xxx-xxxx).[2]
History[edit]
For many years, French subscribers’ telephone numbers consisted of eight digits (including the one-digit area code 1 for all of Paris and its surrounding departments, or a two-digit area code from 20 to 99 for other metropolitan departments; this area code was dialed only after the trunk code 16). The territories of Overseas France all had their own local numbering plans and used their own country codes but no area codes, and calls between different territories or Metropolitan France required a dialing international call using the international call prefix 19 followed by the country code, area code, and subscriber number.
But that system began to run out of numbers in the 1980s, leading to the adoption of a new «eight-digit» numbering plan on 25 October 1985.[3] On that date, France changed to a system of two zones, one for Paris and the surrounding Île-de-France and another for the other departments.[4] Outside Paris, the old area code was incorporated into the subscriber’s eight-digit number; for Paris, the area code 1 was retained, and a 4 was prefixed to seven-digit numbers, meaning that a subscriber’s number could begin with 40, for example 4056 1873, with the trunk prefix 16 required for calls from the rest of France.[5] For numbers in the Île-de-France surrounding Paris, the old codes 3x and 6x joined the old seven-digit numbers to become eight-digit numbers and were assigned to the Paris area code 1. To call the rest of France from Paris, however, the trunk prefix 16 had to be dialed before the eight-digit number, followed by the area code for Paris 1 and the eight-digit number.
On 18 October 1996, this changed to the present «ten-digit» system (including the default one-digit leading trunk code 0), in which each call is dialed using all ten digits, this national scheme being also extended to cover Overseas France in a single area.[6] Area codes were abolished, and since then France has had a closed numbering plan, where all local or national calls require dialing the leading trunk code.
Following liberalisation in 1998, subscribers (first deployed on land lines and rapidly extended to all mobile networks) could access different carriers by replacing the leading trunk code 0 (omitted from numbers when called from outside France) with another carrier selection code (one digit from 2 to 9, or four digits 16xx). For example, Cegetel required subscribers to dial 7; e.g., Paris 71 xx xx xx xx, instead of 01 xx xx xx xx. Similarly, the international access code using Cegetel would be 70 instead of 00 by replacing the first 0.[7] Since then, the carrier selection code still exists, but carrier preselection (and number portability) is offered by default on all subscriber lines, and the one-digit carrier selection is rarely used. As well, several important national operators merged, and the four-digit carrier selection only persists for subscribers of various international service providers (most of them for mobile telephony, but these carrier selection prefixes are often dialed internally by a terminal device and callers don’t need to care about it, unless they want to select carriers for different services). Additionally, call fees no longer depend on distance throughout the French numbering plan, so carrier selection remains used only for international calls.
The 09 prefix was introduced for non-geographic numbers and special services in September 2006[8] and older numbers such as 08 7x xx xx xx (used for VoIP in Internet boxes) were replaced by 09 5x xx xx xx (telephone service offered by Internet service provider Free, later followed by other French ISPs).[citation needed]
The national information service 12 was closed in 2005 which lead to the creation of many new information services 118 xxx. They cost €3 per call plus €3 per minute.
Defunct prefixes[edit]
Changed in 1996:
- 16 — Long distance prefix — Changed to: 0
- 19 — International prefix — Changed to: 00
The second dial tone was also removed. Dialling procedures now reflect ETSI and ITU recommendations.
Overseas departments and territories[edit]
The French overseas departments (départements d’outre mer or DOM) have separate country codes from metropolitan France, with Réunion being assigned the code 262[9] while Guadeloupe, French Guiana and Martinique were assigned the codes 590, 594 and 596 respectively.[10] Until 1996, the use of the international access code 19 and country code was required for calls from metropolitan France.[1] For example, to call Guadeloupe from metropolitan France, a subscriber would dial 19 590 xxx xxx, 590 being the country code.[11] This included the islands of Saint Barthelemy and Saint Martin, which later separated from Guadeloupe to become collectivities, although they still use the same country code. By contrast, calls to metropolitan France from the overseas departments only required the use of the trunk code 16.[1]
However, under the new present French numbering plan, direct dialling was introduced for calls between the DOMs (including collectivités territoriales) and metropolitan France, requiring only the ‘0’ to be dialed, with the country code being used as a geographical area code.[6] Despite this, the 33 country code was not adopted for calls to the DOMs from the rest of the world, because of technical difficulties with operators in neighbouring countries, for example, calls to Réunion from Mauritius would have to be routed via metropolitan France, adversely affecting voice quality as well as increasing call costs.[12]
In 2001, telephone numbers in the DOMs changed to the same ten-digit format as metropolitan France, with new prefixes beginning with the digit ‘6’ being adopted for mobile phone services:
Guadeloupe, Saint-Barthélemy and Saint-Martin[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 590 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 690 xx xx xx or 0 691 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +590 590 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +590 690 xx xx xx or +590 691 xx xx xx
French Guiana[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 594 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 694 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +594 594 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +594 694 xx xx xx
Martinique[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 596 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 696 xx xx xx or 0 697 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +596 596 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +596 696 xx xx xx or +596 697 xx xx xx
Réunion[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 262 xx xx xx or 0 263 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 692 xx xx xx or 0 693 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +262 262 xx xx xx or +262 263 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +262 692 xx xx xx or +262 693 xx xx xx
Others[edit]
Before 30 March 2007 the collectivité départementale of Mayotte used country code +269, shared with the Comoros:
- From France, including Mayotte: 0 269 xx xx xx
- From Comoros: xx xx xx
- Outside France and Comoros: +269 xx xx xx
On 30 March 2007 Mayotte adopted the +262 code, used by Réunion, and a new numbering range was introduced for mobile phones:
- From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 269 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 639 xx xx xx
- Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +262 269 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +262 639 xx xx xx
Calls to Saint Pierre and Miquelon require only ‘0’, country code and the subscriber’s six-digit number, e.g.:
- From France: 0 508 xx xx xx
- Outside France: +508 xx xx xx
Calls to and from the territoires d’outre mer, however, require full international dialing, hence the international access code and country code must be used:
- Paris from New Caledonia: 00 33 1 xx xx xx xx
- New Caledonia from Paris: 00 687 xx xx xx
Andorra and Monaco[edit]
Until 17 December 1994, Andorra formed part of the French numbering plan, with calls from France requiring the prefix 628,[13] (or 16 628 from Paris).[14] Those from the rest of the world were made using +33 628,[15] except from Spain, which were made using the prefix 9738.[14] On that date, the principality adopted the country code +376.[16] Consequently, all calls from France to Andorra had to be dialled in international format, using the prefix 19 376.[17] This was later changed to 00 376, along with the second French reform of 1996 to the newer «ten-digit» plan.[18]
On 21 June 1996, Monaco similarly adopted its own country code +377, replacing access from France (+33 93).[19]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Le téléphone refait son numéro. Fin 1996, la numérotation passera à dix chiffres, sans le 16 et le 19 Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Libération, 17 May 1995
- ^ «ANNU.COM — L’annuaire inversé !». www.annu.com. Retrieved 2019-09-30.
- ^ Médiaspouvoirs Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Issues 1-5, Bayard-Presse, 1985, page 146
- ^ Nouvelle numérotation, nouvelle communication: le succès sur toute la ligne Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Simone Muet, Jacques Hintzy, Documentation française, 1986, page 78
- ^ Nonconventional Energy Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Ashok V. Desai, New Age International, 1990
- ^ a b Téléphone : 10 chiffres pour préparer l’arrivée de la concurrence et des nouveaux services Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Les Echos, 18 October 1996
- ^ Cegetel inaugure le premier service grand public concurrent de France Télécom Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Les Echos, 2 February 1998
- ^ «art-telecom» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-09-14. Retrieved 2019-02-03.
- ^ White Book Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Volume 2, Part 1, International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee, International Telecommunication Union, 1969, page 29
- ^ Yellow book: International telephone service : operation Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, International Telecommunication Union, International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee. Plenary Assembly International Telecommunication Union, 1981, page 87
- ^ Cruising World Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, August 1991, page 103
- ^ Nouvelle numérotation téléphonique et départements d’outre-mer Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Sénat, 2 January 1997
- ^ Fodor’s Europe Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Eugene Fodor, D. McKay., 1993, page 52
- ^ a b Mediterranean Europe Archived 2022-03-26 at the Wayback Machine, Lonely Planet, 1995, page 104
- ^ The Merrill Lynch Euromoney Directory Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Euromoney Publications PLC, 1988, page 1
- ^ Japan Directory Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Issue 1, Japan Press, 1995, page 44
- ^ Fodor’s Europe Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Eugene Fodor, D. McKay, 1996, page 35
- ^ Paris Match Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Issues 2519-2522, 1997, page 304
- ^ Hydrographic Review, Volume 73, International Hydrographic Bureau, 1996, page 179
External links[edit]
- ARCEP: La numérotation, French official plan
- French Phone system by Whitepages
- World Telephone Numbering Guide: France
 5 geographic zones | |
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Country | France |
| Continent | Europe |
| Regulator | ARCEP |
| Type | Closed |
| NSN length | 9 |
| Format | 0x xx xx xx xx |
| Access codes | |
| Country calling code | 33 |
| International call prefix | 00 |
| Trunk prefix | 0 |
The French telephone numbering plan is used in Metropolitan France, French overseas departments and some overseas collectivities.
France uses a ten-digit closed numbering plan, where the first two digits denote a geographic area, mobile or non-geographic number.
- 01 Île-de-France
- 02 Northwest France
- 03 Northeast France
- 04 Southeast France
- 05 Southwest France
- 06 Mobile phone services
- 07 Mobile phone services
- 08 Special phone numbers: Freephone (numéro vert) and shared-cost services.
- 09 Non-geographic number (used by Voice over IP services)
All geographic numbers are dialed in the ten-digit format, even for local calls. The international access code is the International Telecommunication Union’s recommended 00.[1]
When calling France from abroad, the leading zero should be omitted: for example, to call a number in Southwest France, one would dial +33 5 xx xx xx xx.
French people usually state phone numbers as a sequence of five double-digit numbers, e.g., 0x xx xx xx xx (and not, for example, 0 xxx-xxx-xxx or 0xxx-xx-xxxx or 0xx-xxx-xxxx).[2]
History[edit]
For many years, French subscribers’ telephone numbers consisted of eight digits (including the one-digit area code 1 for all of Paris and its surrounding departments, or a two-digit area code from 20 to 99 for other metropolitan departments; this area code was dialed only after the trunk code 16). The territories of Overseas France all had their own local numbering plans and used their own country codes but no area codes, and calls between different territories or Metropolitan France required a dialing international call using the international call prefix 19 followed by the country code, area code, and subscriber number.
But that system began to run out of numbers in the 1980s, leading to the adoption of a new «eight-digit» numbering plan on 25 October 1985.[3] On that date, France changed to a system of two zones, one for Paris and the surrounding Île-de-France and another for the other departments.[4] Outside Paris, the old area code was incorporated into the subscriber’s eight-digit number; for Paris, the area code 1 was retained, and a 4 was prefixed to seven-digit numbers, meaning that a subscriber’s number could begin with 40, for example 4056 1873, with the trunk prefix 16 required for calls from the rest of France.[5] For numbers in the Île-de-France surrounding Paris, the old codes 3x and 6x joined the old seven-digit numbers to become eight-digit numbers and were assigned to the Paris area code 1. To call the rest of France from Paris, however, the trunk prefix 16 had to be dialed before the eight-digit number, followed by the area code for Paris 1 and the eight-digit number.
On 18 October 1996, this changed to the present «ten-digit» system (including the default one-digit leading trunk code 0), in which each call is dialed using all ten digits, this national scheme being also extended to cover Overseas France in a single area.[6] Area codes were abolished, and since then France has had a closed numbering plan, where all local or national calls require dialing the leading trunk code.
Following liberalisation in 1998, subscribers (first deployed on land lines and rapidly extended to all mobile networks) could access different carriers by replacing the leading trunk code 0 (omitted from numbers when called from outside France) with another carrier selection code (one digit from 2 to 9, or four digits 16xx). For example, Cegetel required subscribers to dial 7; e.g., Paris 71 xx xx xx xx, instead of 01 xx xx xx xx. Similarly, the international access code using Cegetel would be 70 instead of 00 by replacing the first 0.[7] Since then, the carrier selection code still exists, but carrier preselection (and number portability) is offered by default on all subscriber lines, and the one-digit carrier selection is rarely used. As well, several important national operators merged, and the four-digit carrier selection only persists for subscribers of various international service providers (most of them for mobile telephony, but these carrier selection prefixes are often dialed internally by a terminal device and callers don’t need to care about it, unless they want to select carriers for different services). Additionally, call fees no longer depend on distance throughout the French numbering plan, so carrier selection remains used only for international calls.
The 09 prefix was introduced for non-geographic numbers and special services in September 2006[8] and older numbers such as 08 7x xx xx xx (used for VoIP in Internet boxes) were replaced by 09 5x xx xx xx (telephone service offered by Internet service provider Free, later followed by other French ISPs).[citation needed]
The national information service 12 was closed in 2005 which lead to the creation of many new information services 118 xxx. They cost €3 per call plus €3 per minute.
Defunct prefixes[edit]
Changed in 1996:
- 16 — Long distance prefix — Changed to: 0
- 19 — International prefix — Changed to: 00
The second dial tone was also removed. Dialling procedures now reflect ETSI and ITU recommendations.
Overseas departments and territories[edit]
The French overseas departments (départements d’outre mer or DOM) have separate country codes from metropolitan France, with Réunion being assigned the code 262[9] while Guadeloupe, French Guiana and Martinique were assigned the codes 590, 594 and 596 respectively.[10] Until 1996, the use of the international access code 19 and country code was required for calls from metropolitan France.[1] For example, to call Guadeloupe from metropolitan France, a subscriber would dial 19 590 xxx xxx, 590 being the country code.[11] This included the islands of Saint Barthelemy and Saint Martin, which later separated from Guadeloupe to become collectivities, although they still use the same country code. By contrast, calls to metropolitan France from the overseas departments only required the use of the trunk code 16.[1]
However, under the new present French numbering plan, direct dialling was introduced for calls between the DOMs (including collectivités territoriales) and metropolitan France, requiring only the ‘0’ to be dialed, with the country code being used as a geographical area code.[6] Despite this, the 33 country code was not adopted for calls to the DOMs from the rest of the world, because of technical difficulties with operators in neighbouring countries, for example, calls to Réunion from Mauritius would have to be routed via metropolitan France, adversely affecting voice quality as well as increasing call costs.[12]
In 2001, telephone numbers in the DOMs changed to the same ten-digit format as metropolitan France, with new prefixes beginning with the digit ‘6’ being adopted for mobile phone services:
Guadeloupe, Saint-Barthélemy and Saint-Martin[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 590 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 690 xx xx xx or 0 691 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +590 590 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +590 690 xx xx xx or +590 691 xx xx xx
French Guiana[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 594 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 694 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +594 594 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +594 694 xx xx xx
Martinique[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 596 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 696 xx xx xx or 0 697 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +596 596 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +596 696 xx xx xx or +596 697 xx xx xx
Réunion[edit]
From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 262 xx xx xx or 0 263 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 692 xx xx xx or 0 693 xx xx xx
Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +262 262 xx xx xx or +262 263 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +262 692 xx xx xx or +262 693 xx xx xx
Others[edit]
Before 30 March 2007 the collectivité départementale of Mayotte used country code +269, shared with the Comoros:
- From France, including Mayotte: 0 269 xx xx xx
- From Comoros: xx xx xx
- Outside France and Comoros: +269 xx xx xx
On 30 March 2007 Mayotte adopted the +262 code, used by Réunion, and a new numbering range was introduced for mobile phones:
- From France:
- Fixed phone line: 0 269 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: 0 639 xx xx xx
- Outside France:
- Fixed phone line: +262 269 xx xx xx
- Mobile phone line: +262 639 xx xx xx
Calls to Saint Pierre and Miquelon require only ‘0’, country code and the subscriber’s six-digit number, e.g.:
- From France: 0 508 xx xx xx
- Outside France: +508 xx xx xx
Calls to and from the territoires d’outre mer, however, require full international dialing, hence the international access code and country code must be used:
- Paris from New Caledonia: 00 33 1 xx xx xx xx
- New Caledonia from Paris: 00 687 xx xx xx
Andorra and Monaco[edit]
Until 17 December 1994, Andorra formed part of the French numbering plan, with calls from France requiring the prefix 628,[13] (or 16 628 from Paris).[14] Those from the rest of the world were made using +33 628,[15] except from Spain, which were made using the prefix 9738.[14] On that date, the principality adopted the country code +376.[16] Consequently, all calls from France to Andorra had to be dialled in international format, using the prefix 19 376.[17] This was later changed to 00 376, along with the second French reform of 1996 to the newer «ten-digit» plan.[18]
On 21 June 1996, Monaco similarly adopted its own country code +377, replacing access from France (+33 93).[19]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Le téléphone refait son numéro. Fin 1996, la numérotation passera à dix chiffres, sans le 16 et le 19 Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Libération, 17 May 1995
- ^ «ANNU.COM — L’annuaire inversé !». www.annu.com. Retrieved 2019-09-30.
- ^ Médiaspouvoirs Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Issues 1-5, Bayard-Presse, 1985, page 146
- ^ Nouvelle numérotation, nouvelle communication: le succès sur toute la ligne Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Simone Muet, Jacques Hintzy, Documentation française, 1986, page 78
- ^ Nonconventional Energy Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Ashok V. Desai, New Age International, 1990
- ^ a b Téléphone : 10 chiffres pour préparer l’arrivée de la concurrence et des nouveaux services Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Les Echos, 18 October 1996
- ^ Cegetel inaugure le premier service grand public concurrent de France Télécom Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Les Echos, 2 February 1998
- ^ «art-telecom» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-09-14. Retrieved 2019-02-03.
- ^ White Book Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Volume 2, Part 1, International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee, International Telecommunication Union, 1969, page 29
- ^ Yellow book: International telephone service : operation Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, International Telecommunication Union, International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee. Plenary Assembly International Telecommunication Union, 1981, page 87
- ^ Cruising World Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, August 1991, page 103
- ^ Nouvelle numérotation téléphonique et départements d’outre-mer Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Sénat, 2 January 1997
- ^ Fodor’s Europe Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Eugene Fodor, D. McKay., 1993, page 52
- ^ a b Mediterranean Europe Archived 2022-03-26 at the Wayback Machine, Lonely Planet, 1995, page 104
- ^ The Merrill Lynch Euromoney Directory Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Euromoney Publications PLC, 1988, page 1
- ^ Japan Directory Archived 2020-08-08 at the Wayback Machine, Issue 1, Japan Press, 1995, page 44
- ^ Fodor’s Europe Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Eugene Fodor, D. McKay, 1996, page 35
- ^ Paris Match Archived 2022-10-31 at the Wayback Machine, Issues 2519-2522, 1997, page 304
- ^ Hydrographic Review, Volume 73, International Hydrographic Bureau, 1996, page 179
External links[edit]
- ARCEP: La numérotation, French official plan
- French Phone system by Whitepages
- World Telephone Numbering Guide: France
Кратко о том как звонить в Францию
C мобильного в Францию из России
+ 33 [код города | код оператора] + [номер телефона]
С стационарного в Францию из России
8 10 33 [код города | код оператора] + [номер телефона]
С домашнего вФранцию из России
8 10 33 [код города | код оператора] + [номер телефона]
Из офиса в Францию из России
9 8 10 33 [код города | код оператора] + [номер телефона]
Важные заметки при наборе номера
- 8 — код выхода на межгородскую связь
- 10 — код выхода на международную связь
- 33 — телефонный код Франции
- 9 — как правило, данный код применяется для выхода на городскую связь
Инструкция на английском языке можно получить по ссылке:
how to call France
Как позвонить в Францию и ее города
С мобильного телефона из России в Францию
С городского телефона из России в Францию
Из офиса в России в Францию
|
Список городов и информации Франции
(Код 33)
Почтовые индексы России → Определение оператора и региона по номеру телефона → Телефонные коды стран мира → Телефонный код Франция. Коды городов Франция
Телефонный код Франция. Коды городов Франция
Телефонный код Франция 33
Как позвонить в Франция
С мобильного телефона в России:
+33-(код города)-(номер абонента)
Со стационарного телефона в России:
8-10-(33)-(код города)-(номер абонента)
Телефонные коды городов Франция
-
Авиньон 49 Ажен 553 Алансон 233 Альби 563 Амьен 322 Ангулем 545 Анже 241 Аннеси 450 Антиб 493 Арль 490 Аррас 321 Аяччо (Корсика) 495 Бар-ле-Дюк 329 Безансон 381 Белен 479 Бельфор 384 Блуа 254 Бобиньи 14 Бове 344 Бордо 556 Бурж 248 Бурк-ан-Брас 474 Валянс 475 Ванн 297 Везуль 384 Версаль 13 Вильфранш-Сюр-Сон 474 Вьенна 474 Гап 492 Гере 555 Гренобль 476 Дижон 380 Динь 492 Драгиньян 494 Дюнкерк 328 Кан 231 -
Каор 565 Каркассон 468 Кемпер 298 Клермон-Ферран 473 Кольмар 389 Кретей 14 Ла-Рош-Сюр-Ион 251 Ла-Рошель 546 Лаваль 243 Лан 323 Ле-Ман 243 Ле-Пюи 471 Ленгви 382 Либурн 557 Лилль 320 Лимож 544 Лион 437 Лон-Ле-Сонье 384 Макон 385 Манд 466 Марсель 491 Мелен 160 Мец 387 Мон-де-Марсан 558 Монблан 563 Монпелье 467 Монте Карло 493 Мулен 470 Нанси 383 Нант 240 Нантер 14 Невер 386 Ним 466 Ницца 493 Ньор 549 Оза 562 -
Орийак 471 Орлеан 238 Осер 386 Оуа 561 Париж 1 Периге 553 Перпиньян 468 По 559 Понтуаз 13 Прива 475 Пуатье 549 Пюи-де-Дрм 3371 Ренн 223 Родез 565 Руан 235 Рубе 327 Сен Брие 296 Сен-Ло 233 Сент Этьен 477 Страсбург 390 Тарб 562 Труа 325 Тулон 498 Тулуза 534 Тур 247 Тьонвиль 382 Тюль 555 Фуа 561 Шамберн 479 Шартр 237 Шатору 254 Шомон 325 Эвре 232 Эври 16 Экс Ан Прованс 442 Эпиналь 329
-
Авиньон 49 Ажен 553 Алансон 233 Альби 563 Амьен 322 Ангулем 545 Анже 241 Аннеси 450 Антиб 493 Арль 490 Аррас 321 Аяччо (Корсика) 495 Бар-ле-Дюк 329 Безансон 381 Белен 479 Бельфор 384 Блуа 254 Бобиньи 14 Бове 344 Бордо 556 Бурж 248 Бурк-ан-Брас 474 Валянс 475 Ванн 297 Везуль 384 Версаль 13 Вильфранш-Сюр-Сон 474 Вьенна 474 Гап 492 Гере 555 Гренобль 476 Дижон 380 Динь 492 Драгиньян 494 Дюнкерк 328 Кан 231 Каор 565 Каркассон 468 Кемпер 298 Клермон-Ферран 473 Кольмар 389 Кретей 14 Ла-Рош-Сюр-Ион 251 Ла-Рошель 546 Лаваль 243 Лан 323 Ле-Ман 243 Ле-Пюи 471 Ленгви 382 Либурн 557 Лилль 320 Лимож 544 Лион 437 Лон-Ле-Сонье 384 -
Макон 385 Манд 466 Марсель 491 Мелен 160 Мец 387 Мон-де-Марсан 558 Монблан 563 Монпелье 467 Монте Карло 493 Мулен 470 Нанси 383 Нант 240 Нантер 14 Невер 386 Ним 466 Ницца 493 Ньор 549 Оза 562 Орийак 471 Орлеан 238 Осер 386 Оуа 561 Париж 1 Периге 553 Перпиньян 468 По 559 Понтуаз 13 Прива 475 Пуатье 549 Пюи-де-Дрм 3371 Ренн 223 Родез 565 Руан 235 Рубе 327 Сен Брие 296 Сен-Ло 233 Сент Этьен 477 Страсбург 390 Тарб 562 Труа 325 Тулон 498 Тулуза 534 Тур 247 Тьонвиль 382 Тюль 555 Фуа 561 Шамберн 479 Шартр 237 Шатору 254 Шомон 325 Эвре 232 Эври 16 Экс Ан Прованс 442 Эпиналь 329
